Guides For Song Editor Recording On GarageBand
Guides For Song Editor Recording On GarageBand - You can edit regions from GarageBand recording, Apple Loops, and imported audio files in the editor. The editor has its own ruler, playhead, and grid. The types of edits you can make depend on the type of region:
Audio regions: You can split, join, rename, music cutter and transpose audio regions created from audio Apple Loops or recordings (blue) in the Audio Editor. You can also set whether audio recordings and loops follow the project tempo, adjust their tuning, and enhance their timing.
MIDI regions: You can rename and transpose MIDI regions, enhance their timing, and edit notes and controller information in the Piano Roll Editor. You can also view and edit MIDI regions as music notation in the Score Editor.
Drummer regions: You can choose drum genres, drummers, and presets in the Library, and edit Drummer region settings to control different aspects of the drummer’s performance in the Drummer Editor.
Audio files: You can split, join, and rename regions from imported audio files (orange) in the Audio Editor.
The editor is like a microscope showing a close-up view of part of a track in the Tracks area. For audio tracks, the Audio Editor shows the audio waveform of the regions in the track. For software instrument tracks, the Piano Roll Editor shows the regions in the track in a graphical view, while the Score Editor shows them in a music notation view. For Drummer tracks, the Library shows the genre, drummer, and presets, and the Drummer editor shows performance parameters for the current region.
You can zoom the editor independently from the Tracks area using its zoom slider. You can also resize the editor to give yourself more room to work.
Resize the editor vertically
Zoom the editor
Edit Audio Regions In The GarageBand Recording
The Audio Editor shows a close-up view of part of an audio track, displaying the audio waveform of the track’s regions in a time grid.
In the Audio Editor, you can move and trim audio regions, split and join them, and edit them in other ways. You can scroll and zoom the Audio Editor, and zoom the amplitude of the waveforms in audio regions. Edits you make in the Audio Editor are nondestructive, so you can always return to your original recordings.
You can also correct the pitch of audio material in the Audio Editor. For more information, see Correct the pitch of regions on an audio track. Using Flex Time, you can edit the timing of audio material in the Audio Editor. For more information, see Edit the timing of notes and beats.
Open the Audio Editor
Do one of the following:
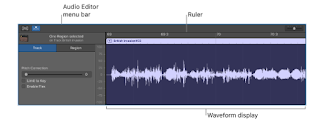
The Audio Editor opens below the Tracks area. Along the top of the Audio Editor is a ruler showing time divisions, and a menu bar with Flex, Catch, and zoom controls. The main area of the Audio Editor shows the audio waveform of the regions in the selected audio track.
Vertically resize the Audio Editor
Zoom the Audio Editor horizontally
Close the Audio Editor
When the track is selected (and no individual region is selected), the following controls appear in the Audio Editor inspector:
When one or more regions are selected, the following controls appear in the Audio Editor inspector to the left of the waveform:
Read How To Record Audio On GarageBand
Edit Audio Regions In The Audio Editor
You can cut or copy an audio region or region segment in the Audio Editor and paste the copy at a different time position
Cut an audio region
Copy an audio region
Do one of the following:
Paste an audio region
Move an audio region
Split a section of an audio region
1. Place the pointer over the lower half of the region. The pointer changes to a Marquee pointer.
2. Drag the Marquee pointer over the part of the region you want to split. The part of the region outlined by the Marquee pointer is split. You can press Delete to delete it, or move the pointer over the upper half of the region, then drag the split part to another position.
Audio Trimmer Region
1. Place the pointer over the lower-left or lower-right edge of the region. The pointer changes to a Trim pointer.
2. Drag the pointer over the part you want to trim. As you drag, the help tag shows the region length and the amount by which it’s trimmed.
Quantize The Timing Of Audio Regions
You can quantize, or automatically correct, the timing of regions on an audio track. This technique is especially useful when regions on the track contain the right notes but are not perfectly in time with the project tempo.
When you quantize the timing, selected regions on the selected track are adjusted to the selected note value. You can quantize the timing of regions with drums, single-note instruments, and chordal or polyphonic instruments.
If the track contains imported audio files (orange), and you want to quantize the timing of the audio files, the Follow Tempo & Pitch checkbox needs to be selected for each audio file.
Quantize the timing of selected audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the audio regions you want to quantize. The regions need to be on the same audio track.
2. Make sure the Region tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Choose the note value to use as the basis for timing quantization from the Time Quantize pop-up menu.
4. Drag the Strength slider to the left to decrease the strength of quantization.
Transpose Audio Regions
You can transpose audio, transpose chords, transpose music in the Audio Editor. Audio regions can be transposed up or down by up to 12 semitones. A semitone is the smallest distance between two musical notes. Notes with the same name repeat every 12 semitones, called an octave.
Transpose selected audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the regions you want to correct.
2. Make sure the Region tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Drag the Transpose slider left or right to transpose the regions in semitones.
Correct The Pitch Of Regions On An Audio Track
How to change pitch in GarageBand? You can adjust (correct) the tuning of an audio track. This process is especially useful when you record audio regions that have the right “feel” and timing but aren’t perfectly in tune.
When you correct the tuning, all regions on the selected track (both your own recordings and loops) are adjusted. Adjusting the tuning can produce accurate results only for single-note (monophonic) audio regions, so be sure the track doesn’t include regions with chords or unpitched sounds.
By default, notes are adjusted to the closest note on the chromatic (12-note) scale. You can also limit pitch correction to the notes of the project key.
Correct the pitch of audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the regions you want to correct.
2. Make sure the Track tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Drag the Pitch Correction slider to the right to increase the amount of tuning adjustment, or drag it left to decrease the amount of adjustment.
To restrict pitch correction to notes in the project key, select the Limit to Key checkbox.
Edit The Timing Of Notes And Beats
How to make beats on garageband and edit the timing? Flex Time simplifies the process of editing the timing of notes, beats, and other events in audio regions. You can compress or expand the time between specified events without the need for trimming, moving, nudging, or crossfading.
You edit the timing of notes and beats in audio regions using flex markers. In the Audio Editor, you add a flex marker at a specific point of the waveform you want to edit. Clicking a peak in the waveform (called a transient) adds a flex marker that you can use to move that part of the waveform so it lines up with a beat, or with an event on another track. Flex markers are also added at the preceding and following transients.
After adding flex markers to an audio region, you use them to time stretch—compress or expand—the audio material. The boundaries in which time stretching occurs are determined by the preceding and following flex markers, or the region start and end positions if there are no preceding and following flex markers.
Turn on Flex Time
In the Audio Editor, do one of the following:
Time stretch audio using flex markers
1. In the Audio Editor, click the waveform at the point you want to edit. Flex markers appear at the clicked position, and at the location of the preceding and following transients.
2. Do one of the following:
Drag the flex marker to the left.
The audio material is time compressed up to the preceding flex marker, the preceding tempo marker, or the start of the region. The audio material is time expanded up to the following flex marker or the following tempo marker (which can also be the region end position).
If you move the flex marker to the left and it crosses a previous flex marker, the previous flex marker jumps back to the previous transient marker. This behavior allows you to extend the Flex Time editing range to the left. The same behavior occurs if a flex marker crosses a tempo marker.
Drag the flex marker to the right.
The audio material is time expanded up to the preceding flex marker, the preceding tempo marker, or the region start position. The audio material is time compressed up to the following flex marker or the following tempo marker (which can also be the region end position).
If you move the flex marker to the right and it crosses a following flex marker, the following flex marker jumps forward to the next transient marker. This behavior allows you to extend the Flex Time editing range to the right. The same behavior occurs if a flex marker crosses a tempo marker.
Delete, Reset, And Move Flex Markers
When you delete a flex marker, any time changes in the area around the flex marker are either removed (and the audio material returned to its original state), or reset to follow the previous flex marker or region start position and the following flex marker or region end position.
You can delete only those flex markers that were manually added or all flex edits that were carried out on the audio file, which includes audio quantization.
You can also change the position of a flex marker in an audio region without changing the timing of the audio material before or after the flex marker.
Delete a flex marker from an audio region
Do one of the following:
Move a flex marker without time stretching
Audio regions: You can split, join, rename, music cutter and transpose audio regions created from audio Apple Loops or recordings (blue) in the Audio Editor. You can also set whether audio recordings and loops follow the project tempo, adjust their tuning, and enhance their timing.
MIDI regions: You can rename and transpose MIDI regions, enhance their timing, and edit notes and controller information in the Piano Roll Editor. You can also view and edit MIDI regions as music notation in the Score Editor.
Drummer regions: You can choose drum genres, drummers, and presets in the Library, and edit Drummer region settings to control different aspects of the drummer’s performance in the Drummer Editor.
Audio files: You can split, join, and rename regions from imported audio files (orange) in the Audio Editor.
The editor is like a microscope showing a close-up view of part of a track in the Tracks area. For audio tracks, the Audio Editor shows the audio waveform of the regions in the track. For software instrument tracks, the Piano Roll Editor shows the regions in the track in a graphical view, while the Score Editor shows them in a music notation view. For Drummer tracks, the Library shows the genre, drummer, and presets, and the Drummer editor shows performance parameters for the current region.
You can zoom the editor independently from the Tracks area using its zoom slider. You can also resize the editor to give yourself more room to work.
Resize the editor vertically
- Drag the bar at the top of the editor up or down.
Zoom the editor
- Drag the zoom slider located at the right corner of the editor menu bar.
Edit Audio Regions In The GarageBand Recording
The Audio Editor shows a close-up view of part of an audio track, displaying the audio waveform of the track’s regions in a time grid.
In the Audio Editor, you can move and trim audio regions, split and join them, and edit them in other ways. You can scroll and zoom the Audio Editor, and zoom the amplitude of the waveforms in audio regions. Edits you make in the Audio Editor are nondestructive, so you can always return to your original recordings.
You can also correct the pitch of audio material in the Audio Editor. For more information, see Correct the pitch of regions on an audio track. Using Flex Time, you can edit the timing of audio material in the Audio Editor. For more information, see Edit the timing of notes and beats.
Open the Audio Editor
Do one of the following:
- Select an audio track in the Tracks area, then click the Editors button Editors button.
- Select an audio track in the Tracks area, then choose View > Show Editors.
- Double-click an audio region to open it in the Audio Editor.
The Audio Editor opens below the Tracks area. Along the top of the Audio Editor is a ruler showing time divisions, and a menu bar with Flex, Catch, and zoom controls. The main area of the Audio Editor shows the audio waveform of the regions in the selected audio track.
Vertically resize the Audio Editor
- Place the pointer in the bar at the top of the Audio Editor, then drag upward. Drag downward to make the Audio Editor smaller again.
Zoom the Audio Editor horizontally
- Drag the zoom slider in the Audio Editor menu bar left or right.
Close the Audio Editor
- Click the Editors button Editors button in the control bar.
When the track is selected (and no individual region is selected), the following controls appear in the Audio Editor inspector:
- Pitch Correction slider: Determines the amount of pitch correction applied to regions in the track.
- Limit to Key checkbox: Limits pitch correction to notes in the project key.
- Enable Flex checkbox: Turns on flex editing for the track.
When one or more regions are selected, the following controls appear in the Audio Editor inspector to the left of the waveform:
- Region Name field: Edit the name of the selected regions.
- Time Quantize pop-up menu (with Strength slider): Quantize the timing of notes, beats, and other events in the selected regions.
- Transpose slider: Change the pitch of notes in the selected regions.
- Follow Tempo and Pitch checkbox: Sets whether the regions match the project tempo and key.
Read How To Record Audio On GarageBand
Edit Audio Regions In The Audio Editor
You can cut or copy an audio region or region segment in the Audio Editor and paste the copy at a different time position
Cut an audio region
- Select the region, then choose Edit > Cut (or press Delete).
Copy an audio region
Do one of the following:
- Option-drag the region. When you Option-drag an audio region so that it overlaps another region, the overlapped part of the region is cut.
- Select the region, then choose Edit > Copy.
Paste an audio region
- Place the playhead at the point where you want to paste the region, then choose Edit > Paste.
Move an audio region
- Drag the region horizontally. When you move an audio region so that it overlaps another region, the overlapped part of the region is cut.
Split a section of an audio region
1. Place the pointer over the lower half of the region. The pointer changes to a Marquee pointer.
2. Drag the Marquee pointer over the part of the region you want to split. The part of the region outlined by the Marquee pointer is split. You can press Delete to delete it, or move the pointer over the upper half of the region, then drag the split part to another position.
Audio Trimmer Region
1. Place the pointer over the lower-left or lower-right edge of the region. The pointer changes to a Trim pointer.
2. Drag the pointer over the part you want to trim. As you drag, the help tag shows the region length and the amount by which it’s trimmed.
Quantize The Timing Of Audio Regions
You can quantize, or automatically correct, the timing of regions on an audio track. This technique is especially useful when regions on the track contain the right notes but are not perfectly in time with the project tempo.
When you quantize the timing, selected regions on the selected track are adjusted to the selected note value. You can quantize the timing of regions with drums, single-note instruments, and chordal or polyphonic instruments.
If the track contains imported audio files (orange), and you want to quantize the timing of the audio files, the Follow Tempo & Pitch checkbox needs to be selected for each audio file.
Quantize the timing of selected audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the audio regions you want to quantize. The regions need to be on the same audio track.
2. Make sure the Region tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Choose the note value to use as the basis for timing quantization from the Time Quantize pop-up menu.
4. Drag the Strength slider to the left to decrease the strength of quantization.
Transpose Audio Regions
You can transpose audio, transpose chords, transpose music in the Audio Editor. Audio regions can be transposed up or down by up to 12 semitones. A semitone is the smallest distance between two musical notes. Notes with the same name repeat every 12 semitones, called an octave.
Transpose selected audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the regions you want to correct.
2. Make sure the Region tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Drag the Transpose slider left or right to transpose the regions in semitones.
Correct The Pitch Of Regions On An Audio Track
How to change pitch in GarageBand? You can adjust (correct) the tuning of an audio track. This process is especially useful when you record audio regions that have the right “feel” and timing but aren’t perfectly in tune.
When you correct the tuning, all regions on the selected track (both your own recordings and loops) are adjusted. Adjusting the tuning can produce accurate results only for single-note (monophonic) audio regions, so be sure the track doesn’t include regions with chords or unpitched sounds.
By default, notes are adjusted to the closest note on the chromatic (12-note) scale. You can also limit pitch correction to the notes of the project key.
Correct the pitch of audio regions
1. In the Tracks area, select the regions you want to correct.
2. Make sure the Track tab is selected in the Audio Editor inspector.
3. Drag the Pitch Correction slider to the right to increase the amount of tuning adjustment, or drag it left to decrease the amount of adjustment.
To restrict pitch correction to notes in the project key, select the Limit to Key checkbox.
Edit The Timing Of Notes And Beats
How to make beats on garageband and edit the timing? Flex Time simplifies the process of editing the timing of notes, beats, and other events in audio regions. You can compress or expand the time between specified events without the need for trimming, moving, nudging, or crossfading.
You edit the timing of notes and beats in audio regions using flex markers. In the Audio Editor, you add a flex marker at a specific point of the waveform you want to edit. Clicking a peak in the waveform (called a transient) adds a flex marker that you can use to move that part of the waveform so it lines up with a beat, or with an event on another track. Flex markers are also added at the preceding and following transients.
After adding flex markers to an audio region, you use them to time stretch—compress or expand—the audio material. The boundaries in which time stretching occurs are determined by the preceding and following flex markers, or the region start and end positions if there are no preceding and following flex markers.
Turn on Flex Time
In the Audio Editor, do one of the following:
- Select the Enable Flex checkbox in the Audio Editor inspector.
- Click the Show/Hide Flex button Show/Hide Flex button in the Audio Editor menu bar. You can use the Show/Hide Flex button to hide Flex Time edits without disabling Flex Time for the track.
Time stretch audio using flex markers
1. In the Audio Editor, click the waveform at the point you want to edit. Flex markers appear at the clicked position, and at the location of the preceding and following transients.
2. Do one of the following:
Drag the flex marker to the left.
The audio material is time compressed up to the preceding flex marker, the preceding tempo marker, or the start of the region. The audio material is time expanded up to the following flex marker or the following tempo marker (which can also be the region end position).
If you move the flex marker to the left and it crosses a previous flex marker, the previous flex marker jumps back to the previous transient marker. This behavior allows you to extend the Flex Time editing range to the left. The same behavior occurs if a flex marker crosses a tempo marker.
Drag the flex marker to the right.
The audio material is time expanded up to the preceding flex marker, the preceding tempo marker, or the region start position. The audio material is time compressed up to the following flex marker or the following tempo marker (which can also be the region end position).
If you move the flex marker to the right and it crosses a following flex marker, the following flex marker jumps forward to the next transient marker. This behavior allows you to extend the Flex Time editing range to the right. The same behavior occurs if a flex marker crosses a tempo marker.
Delete, Reset, And Move Flex Markers
When you delete a flex marker, any time changes in the area around the flex marker are either removed (and the audio material returned to its original state), or reset to follow the previous flex marker or region start position and the following flex marker or region end position.
You can delete only those flex markers that were manually added or all flex edits that were carried out on the audio file, which includes audio quantization.
You can also change the position of a flex marker in an audio region without changing the timing of the audio material before or after the flex marker.
Delete a flex marker from an audio region
Do one of the following:
- Place the pointer over the flex marker, then click the “x” in the region header.
- Double-click the flex marker.
Move a flex marker without time stretching
- Hold down Option as you drag the flex marker.










Comments
Post a Comment